Hepatitis C is one of the most dangerous viral hepatitis and you can say that it is the deadliest viral disease of all time. This is caused by Hepatitis C Virus (HCV). In this type of hepatitis Liver cirrhosis is the most common. Hepatitis C is known as a Silent killer. Because it is a lifelong illness. It is because 70% of diagnoses are done when the liver has already damaged half of the cells.
Since 2006 the cases of hepatitis C is increased in people aged less than 30 due to the use of drugs that have to be injected into the body via the use of needles. According to the National Institute of Health and the US department of health, 2.7 to 3.9 million people have been affected with chronic Hepatitis.
As far as hepatitis C is concerned, today its ratio of affected people is decreased due to people following the right protocols that can prevent you from Hepatitis. Today scientist has changed the diagnosis and treatment with new discoveries.
Hepatitis C virus Structure:
The structure of HCV is simple but still, its characteristics are important to know for its replication. Hepatitis C structure has:
- Envelop over protein Coat
- Baltimore classification: IV
- Family: Flavivirus
- The single-stranded positive polarity RNA genome
- Have multiple serotypes
- No polymerase
- 9 mature proteins. (only in Hepatitis C)
- Six main genotypes
- Glycoprotein on the surface of the virus.
How is hepatitis C transmitted?
Hepatitis C is caused by the hepatitis C virus. A lot of individual thinks that this virus transmitted through direct contact and always ask that Is hepatitis C contagious? but no this virus spread exactly like hepatitis B and this is why both of these viruses are dangerous for health. HCV Spread through contaminated syringes, blades, and scissors.
When a healthy person injects the same syringe that has already been used can cause Hepatitis with 90% efficiency. HCV is also transmitted through serum, saliva, and other body fluids but most important through blood-to-blood contact. Hepatitis C virus also spreads through sexual contact but now protection makes it easier and that is why this type of spread is less common.
Since 2006 the cases of hepatitis C have increased in people aged less than 30 due to the use of drugs that have to be injected into the body via the use of needles. According to the National Institute of Health and the US department of health, 2.7 to 3.9 million people have been affected with chronic Hepatitis.
Symptoms of hepatitis C:
After the contact and virus are spread to a healthy person, the virus moves to liver cells where it causes hepatocellular injury when it starts to replicate. You might be thinking that the virus itself causes the injury but no, the virus just produces its multiple copies and this hepatocellular injury is caused by a person’s own cytotoxic T cell that is produced in this reaction.
This is just the acute state disturbance while in chronic state, it leads to hepatocellular carcinoma and this stage is called chronic hepatitis. This is just the pathogenesis of Hepatitis C. The symptoms of hepatitis C are divided into two parts.
Acute Hepatitis C:
Typically when hepatitis C can be treated easily and the infection caused by the virus is at the start leads to acute Hepatitis C. Symptoms are:
- Abdominal pain
- Abdominal discomfort
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever
- Fatigue and muscle pain
- Poor appetite
One important thing to notice is these symptoms are common in every hepatitis viral infection. And that is why Acute hepatitis C can be rarely diagnosed.
Chronic hepatitis C:
The acute stage leads to the chronic stage where 60% of damage is done in the liver. Chronic Hepatitis C is formed when acute hepatitis is not treated well or you are unaware that you got hepatitis C virus in the blood. Symptoms are:
- Persistent fever
- Dark-colored urination
- Gray color stool
- Weight loss
- Fluid retention in the abdomen
- Unable to move due to fatigued legs
Some of the chronic symptoms vary from person to person such as itchy legs, confusion, drowsiness, etc.
Laboratory diagnosis of Hepatitis C:
After the symptoms are observed, they are referred to a virologist. Hepatitis C is diagnosed with the following testing performed by experts in the diagnostic Lab.
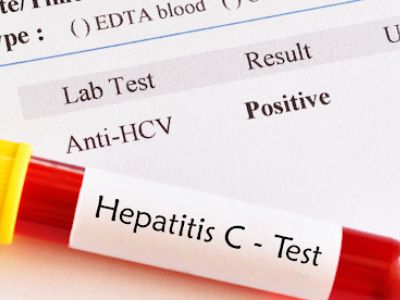
- Serologic testing detects anti-HCV antibodies, which leads to a diagnosis. To determine whether an active infection is present, a PCR-based assay for “viral load” can be used.
- Devices are used to detect antibodies in patient serum which are non-specific.
- ELISA is another technique that can detect antibodies in patient serum but they are specific.
- CMIA(Chemiluminescent Magnetic Microparticle Immunoassay)
- NAT (Nucleic Acid Testing)
Hepatitis C Treatment and prevention:
Hepatitis C is the only hepatitis type that can be treated by antiviral drug therapy. As this virus has symptomatic severity then the doctor also prescribes therapy against the symptoms. Treating nausea and vomiting to prevent water loss from the body. Persistent fever can also be dangerous so medication is also given to the patient.
As chronic hepatitis C mostly causes liver cirrhosis so sometimes Surgeons also recommend liver transplants. That is the reason why hepatitis C is a dangerous viral disease.
According to WHO, there is no vaccination yet discovered to prevent Hepatitis C. There is some prevention that is given below:
- Not share needles.
- Not share shaving blades and Combs.
- Not using someone’s things like toothbrushes, razors, towels, etc.
- Use proper screening of blood and do not touch blood directly with your hands.
- Use gloves and masks if you are medical health professionals. Avoid direct contact with syringes and needles.
- Use fresh fruit and vegetables and drink plenty of water.
And the most important one, do screening of hepatitis twice in 6 months especially screening of Hepatitis B and C.
FAQs:
How do you get hepatitis C?
The most chronic of all hepatitis is Hepatitis C. It is caused by a Single-stranded RNA enveloped virus. It is also transmitted via blood-to-blood contact, syringes, and blades or by body secretion. Transmission can also spread through sexual contact but it’s less common.
Is hepatitis C curable?
Yes, Hepatitis C is curable. It is only hepatitis virus that can be treated with antiviral therapy. Also, it can be prevented by stopping the means of direct blood-to-blood contact and avoiding using other personal things such as towels, blades, and toothbrushes.
Is there any vaccine for Hepatitis C?
According to WHO and health professionals, currently, there is no hepatitis C vaccine, but antiviral therapy is available against hepatitis C and it is although the only cure for hepatitis C. With this you have to follow the prevention that is advised by the doctor.
Conclusion and Doctors Recommendation:
Hepatitis C was one of the dangerous diseases spread throughout the world mainly in 2013-2018 and caused millions of deaths. An estimation of CDC’s 5 thousand cases of acute hepatitis C was reported in 2018. An estimated 2.4 million people in the United States were living with hepatitis C during 2013–2016. Hepatitis C becomes more dangerous when it enters the chronic stage and when it enters chronic hepatitis then it causes liver cirrhosis. You can see that 5-10 percent of people get cirrhosis on an average of 50 chronic carriers.
According to the World Health Organization, over 290 000 individuals died with hepatitis C in 2019, the majority of them died from cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (primary liver cancer). But today in 2020 three of the scientists are awarded Nobel Prize Michael Houghton, Harvey Alter, and Charles Rice and changed the whole scenario and discovered the new treatment against hepatitis C which has saved many lives.
So with these deaths, expert advice to follow up the general protocols that are given for the prevention of not only hepatitis C but also other hepatitis Viruses as well. Pathologists and virologists also make it clear that one must do screening of hepatitis twice in 6 months so that it could prevent the chronic stage and can be treated far more easily.
